Insight 17 Oct 2025
Beyond Automation: 10 CLI Tools Every Linux Admin Should Know in 2025
The Linux command line remains the most powerful and reliable environment for system administrators. While automation frameworks are common, real-world administration still relies on human judgment combined with efficient, transparent tools. Here are ten CLI utilities that make Linux administration in 2025 faster, safer, and more insightful — culminating with a new kind of assistant that brings AI to the terminal without removing human control.
 ayonik engineering
ayonik engineering
1. tmux – Persistent Terminal Sessions
tmux (terminal multiplexer) lets you manage multiple terminal sessions on a Linux server, for example on a jump server. Sessions persist across SSH logins, making it ideal for long-running maintenance tasks or monitoring. Switching between the different sessions can easily be done by key combinations (e.g. Ctrl+b n for next window). Admins can even share sessions for collaborative troubleshooting — a simple, reliable productivity booster.
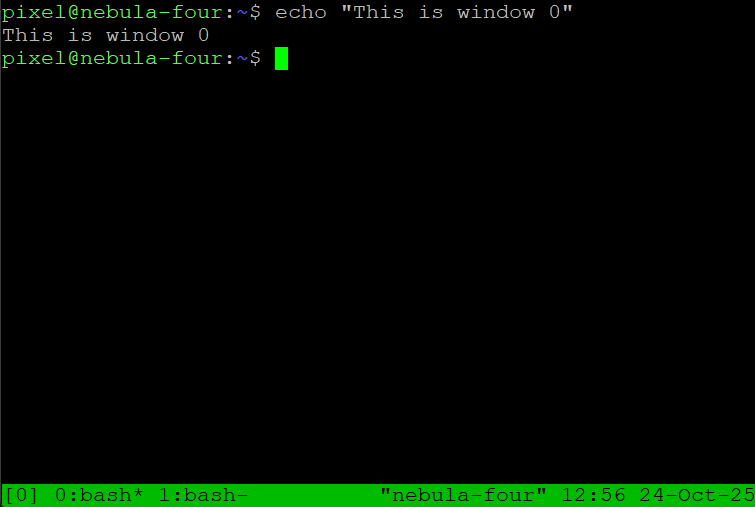
2. ncdu – Disk Usage Analysis at a Glance
ncdu scans file systems and displays directory sizes in an interactive tree view. It runs comfortably over SSH and makes it straightforward to locate large or obsolete files. Perfect for cleaning up production servers or diagnosing unexpected disk consumption.
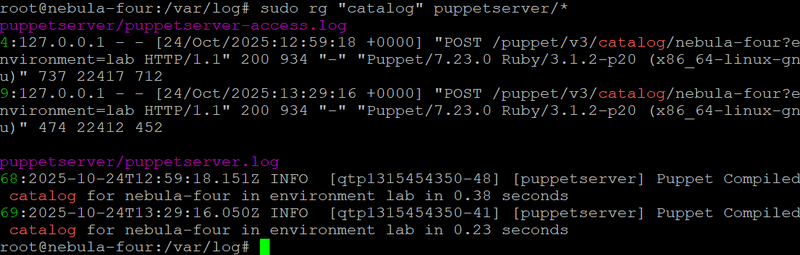
3. ripgrep (rg) – High-Performance Text Search
ripgrep (rg) is a modern reimplementation of grep, built for speed and accuracy. It searches recursively through directories, respects .gitignore rules, and handles large data sets efficiently. For log analysis or code inspection, it’s become the default choice for fast, context-rich searches.
4. bat – Syntax-Aware File Viewing
bat adds syntax highlighting, line numbers, and Git integration to the classic cat command. Readable color themes make configuration files and scripts easier to review in the terminal. It’s especially useful in environments where clarity and accuracy prevent costly errors. On some systems the command is invoked by batcat.
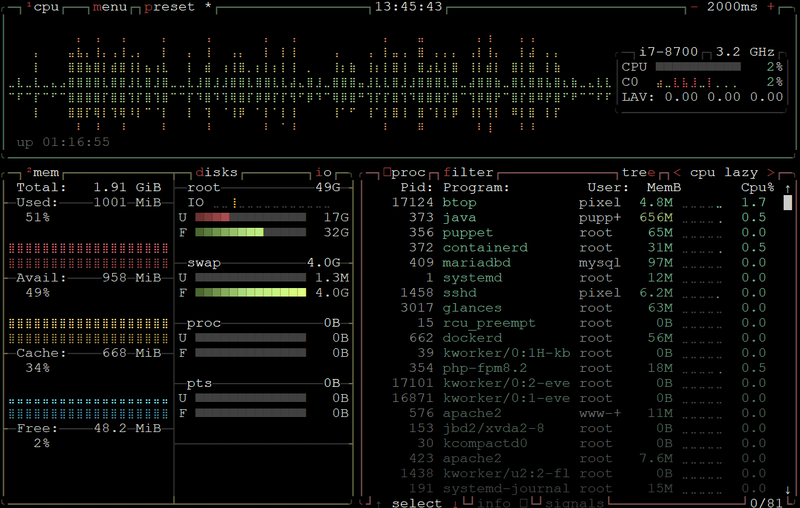
5. btop – Next-Generation System Resource Monitor
btop represents the evolution of classic process monitoring tools like top and htop. While top has been a Unix standard since the 1980s and htop modernized interaction, btop takes it further with a C++-based graphical interface. It provides real-time CPU, memory, I/O, and network statistics in a responsive terminal UI with mouse support and smooth visual graphs. Combining the clarity of top with the usability of a dashboard, btop has become the preferred choice for modern administrators.
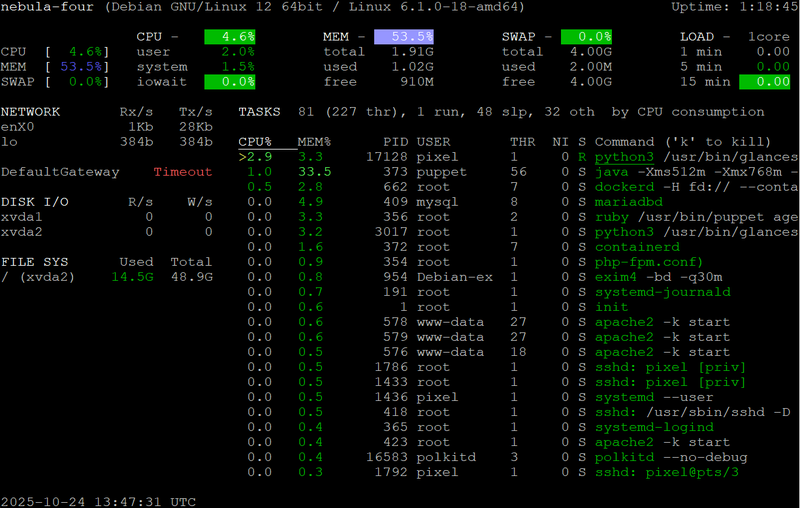
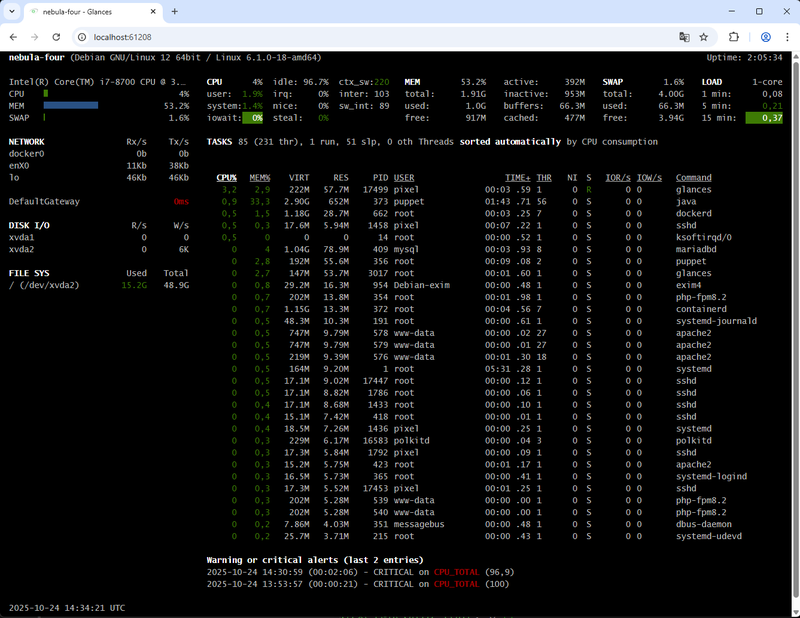
6. glances – System Overview and Remote Monitoring
Glances provides a comprehensive, real-time view of system performance “at a glance.” Built in Python, it tracks CPU, memory, disk I/O, network activity, and running processes in a single interface. It can also collect metrics from remote or export data to Prometheus, InfluxDB, or JSON for use in other dashboards. Glances even includes a lightweight web server, allowing you to monitor systems via a browser. While less visual than btop, its versatility make it a powerful tool for managing multiple machines.
7. restic – Secure, Efficient Backups
restic provides encrypted, deduplicated backups with a strong focus on simplicity and integrity. It supports local and remote storage backends like SFTP and S3, with fast restore capabilities. Admins value its scriptability and confidence that data can be restored reliably when needed most.
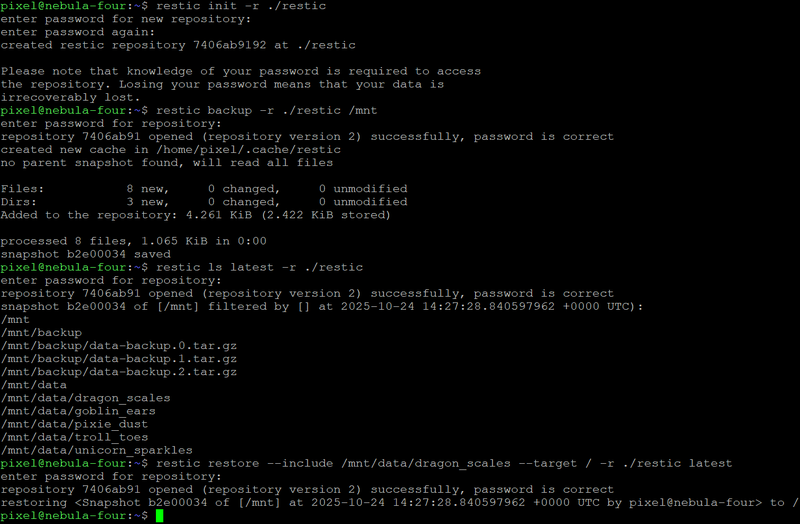
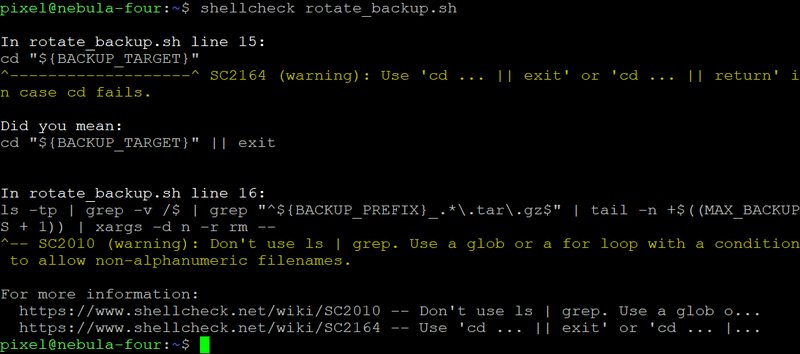
8. shellcheck – Static Analysis for Shell Scripts
Before deploying any script, shellcheck scans it for syntax issues, quoting errors, and unsafe constructs. It highlights problematic lines and links to documentation explaining each warning. Integrating it into CI pipelines is one of the simplest ways to prevent downtime from human mistakes.
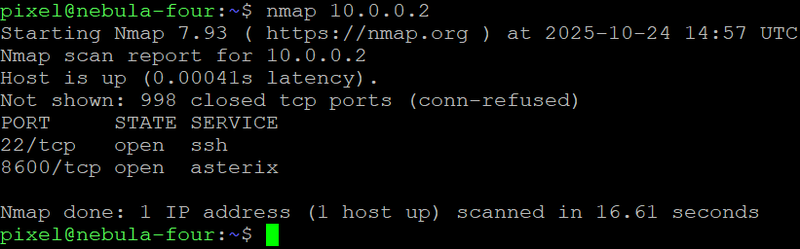
9. nmap – Network Exploration and Security Auditing
nmap remains the gold standard for network scanning and service discovery. It identifies open ports, running services, and potential vulnerabilities across systems. Its scripting engine (NSE) extends functionality for detailed audits — still unmatched for visibility and control.
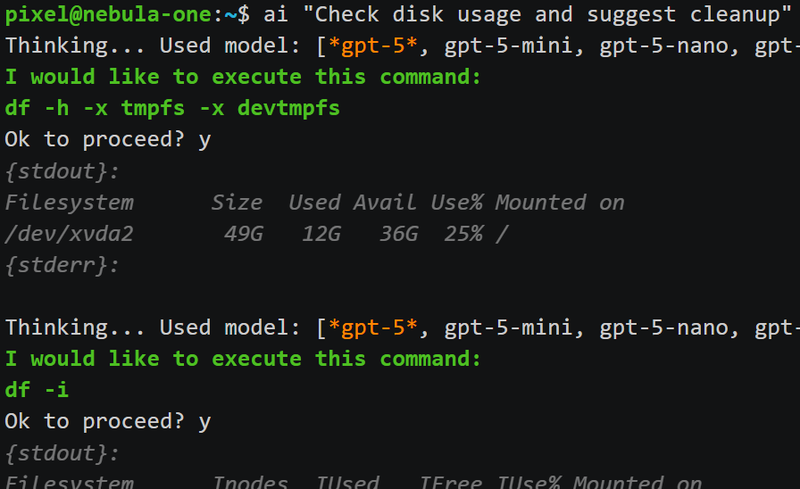
10. Admin Companion – The AI Co-Administrator for Linux
Purpose: Human-in-the-Loop command assistance
While the previous tools enhance efficiency, Admin Companion introduces a new concept: a co-administrator that works alongside you. It understands natural-language requests, proposes precise shell commands, explains their effects, and can execute them — but only after explicit confirmation. This approach not only keeps the admin in full control — it also reduces repetitive effort, simplifies complex tasks, and increases overall efficiency in daily operations.
Key Features
- CLI interface for Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, and RedHat
- Natural-language command generation and explanations
- Secure execution with mandatory user approval
- Transparent, auditable workflow design
Best for: Linux professionals who want to combine their expertise with an AI assistant that enhances accuracy, speed, and understanding — never replacing human judgment.
👉 Learn more at admin-companion.ai
Conclusion
Linux administration in 2025 is about augmentation, not automation. Tools like ripgrep, restic, and shellcheck reduce friction, and Admin Companion extends that same efficiency even further — combining the speed of AI assistance with the oversight and experience of a human administrator. With the right set of CLI tools — and a trusted co-administrator — system management becomes faster, smarter, and more secure than ever.
linux cli tools 2025, system administration, best linux tools, devops productivity, ai linux assistant, admin companion, human in the loop, sysadmin efficiency